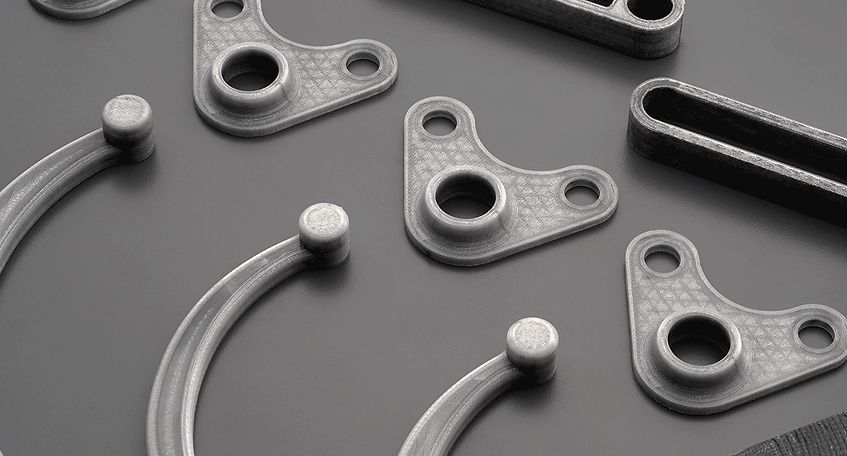
3D Printing Carbon Fiber- Ultimate Guide
3D print with the strength and durability of carbon fiber, plus see which carbon fiber 3D printers do it best. Carbon fiber filaments contain short fibers infused into PLA or ABS to increase strength and stiffness.
When superior mechanical properties, lightweight design, and durability are paramount for your components or products, carbon fiber emerges as an exceptional choice to meet these criteria with precision. Renowned for its remarkable strength-to-weight ratio, carbon fiber stands as the preferred material in high-performance engineering applications, including the manufacturing of shop tools, factory jigs and fixtures, auto body prototypes, and more.
Having gained popularity since the 1960s, 3D printing with carbon fiber has recently garnered significant attention for imparting plastic parts with strength akin to metal, along with heightened resistance to heat, chemicals, and corrosion.
What is Carbon Fiber in 3D Printing?
The specifications for 3D printing carbon fiber filaments must align seamlessly with the characteristics of the base material they are blended with. A crucial consideration is the potential for nozzle blockages in 3D printers due to the presence of fibers, prompting experts to advocate for the use of hardened steel nozzles. Moreover, exceeding a specific threshold of fiber content can compromise the surface finish of the 3D-printed object.
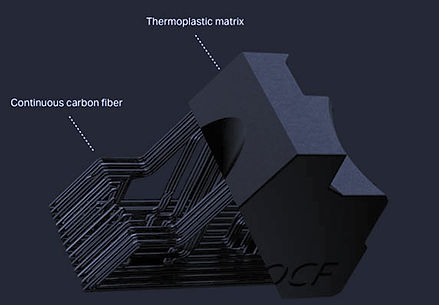
Within the realm of 3D printing, carbon fiber finds application in two primary forms: carbon fiber-reinforced filaments and continuous carbon fiber reinforcement. Filaments reinforced with carbon fiber offer superior strength when compared to their unreinforced counterparts. However, for parts requiring even greater strength, an alternative method known as continuous carbon fiber reinforcement comes into play. This technique involves the use of dual nozzles—one for extruding the filament and the other for extruding the carbon fiber.
As the continuous carbon fiber remains uncut into smaller segments, it retains a heightened level of strength. Impressively, continuous carbon fiber 3D printing showcases robustness to the extent of potentially replacing aluminum, while weighing only half as much. Lastly, strategically placing carbon fiber in accordance with additive manufacturing design principles enables further strengthening of parts while minimizing material consumption.
Benefits of Carbon Fiber 3D Printing

Printing with carbon-fiber-reinforced materials stands out as a preferred choice when elevated physical performance is a paramount consideration, surpassing the capabilities of conventional materials such as PLA, ABS, nylon, or PETG. This preference extends not only to the production of end-use components but also encompasses the creation of manufacturing rigs, jigs, and functional prototypes.
The utilization of carbon fiber in 3D printing brings about a notable enhancement in strength while concurrently reducing overall weight, making it an exceptionally well-suited composite for a diverse array of industries, including automotive, aerospace, and sporting goods. The manifold advantages of carbon fiber-reinforced 3D printing extend beyond the conventional constraints of more commonplace materials.
Significantly, carbon fiber imparts several commendable attributes to 3D-printed objects, thereby solidifying its reputation in the industry. These attributes include:
-
High strength and stiffness
-
Potential metal substitute
-
Exceptional dimensional stability
-
Usable for end-use parts and functional prototypes
-
Resistant to corrosion, heat, oil, and grease
Applications for Carbon Fiber 3D Printed Parts
Carbon fiber 3D printing has revolutionized various industries by offering a unique combination of high strength, lightweight properties, and exceptional resistance to impact, heat, and chemicals. Unlike traditional manufacturing methods, this technology has expanded the possibilities for designing and producing parts that were previously unimaginable.
One of the key advantages of carbon fiber 3D printed parts is their ability to withstand the intense heat generated by automotive and aerospace engine components. In addition, these parts can serve as durable replacements for machined aluminum components, as well as valuable manufacturing aids. The result is the creation of long-lasting, high-impact equipment that meets the stringent requirements of diverse applications.
The versatility of 3D printed carbon fiber composites extends to various industries, including automotive, aerospace, defense, and manufacturing. This technology facilitates the rapid and efficient production of parts with high strength and temperature resistance, coupled with geometric flexibility. By sidestepping traditional machining or molding processes, users can easily fabricate custom parts, replacement components, and functional prototypes.
While 3D printed carbon fiber parts may not entirely replace traditional techniques, they surpass most plastics in terms of strength. This makes them exceptionally useful across a wide range of applications, providing a balance between strength and versatility. The selection of the right manufacturing process, whether molding or 3D printing, depends on factors such as part design, production volume, and specific application requirements.
SLS 3D printing, particularly with chopped fibers, strikes a balance that caters to those seeking robust parts without necessarily requiring the level of complexity found in traditional molded carbon fiber components.